Analog and digital mixers are two different types of audio mixing equipment that are used to combine multiple audio signals and produce a final mixed output. Both types of mixers have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them ultimately depends on the specific needs of the user.
Analog mixers
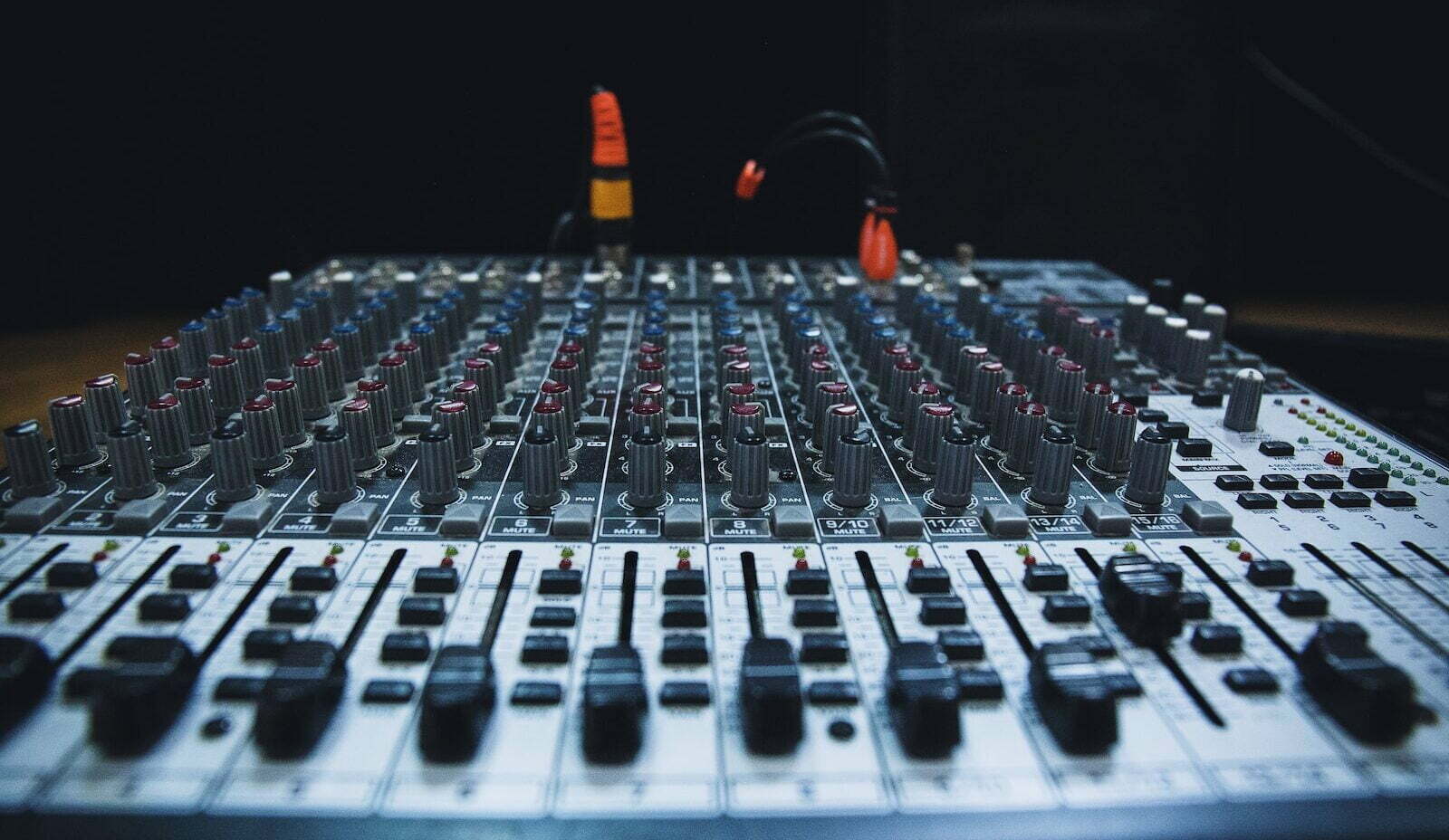
Analog mixers use a purely analog signal path to process audio signals. The mixer takes in audio signals through its inputs, applies various processing functions (such as EQ, compression, and panning) to each channel, and then combines the signals together to produce a final mixed output. The audio signals are processed using physical components, such as resistors, capacitors, and amplifiers, which can introduce a certain level of noise, distortion, and coloration to the sound.
- Advantages of analog mixers:
- Analog mixers are generally considered to have a warmer, more natural sound compared to digital mixers.
- Analog mixers are often simpler and more intuitive to use, with physical knobs and faders that allow for hands-on control of the audio signals.
- Analog mixers are typically less expensive than digital mixers, making them a good choice for users on a budget.
- Disadvantages of analog mixers:
- Analog mixers can be less precise and less consistent in their processing than digital mixers, since they are subject to the limitations of their physical components.
- Analog mixers can be more prone to noise and interference than digital mixers, especially when multiple components are connected together in a chain.
- Analog mixers may require more maintenance over time, as the physical components can wear out and need to be replaced.
Digital mixers
Digital mixers use digital signal processing (DSP) to process audio signals. The mixer takes in audio signals through its inputs, converts them into digital signals using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), applies processing functions to each channel using software algorithms, and then combines the signals together to produce a final mixed output. The audio signals are processed using digital processing chips, which can be programmed to provide precise and consistent processing.
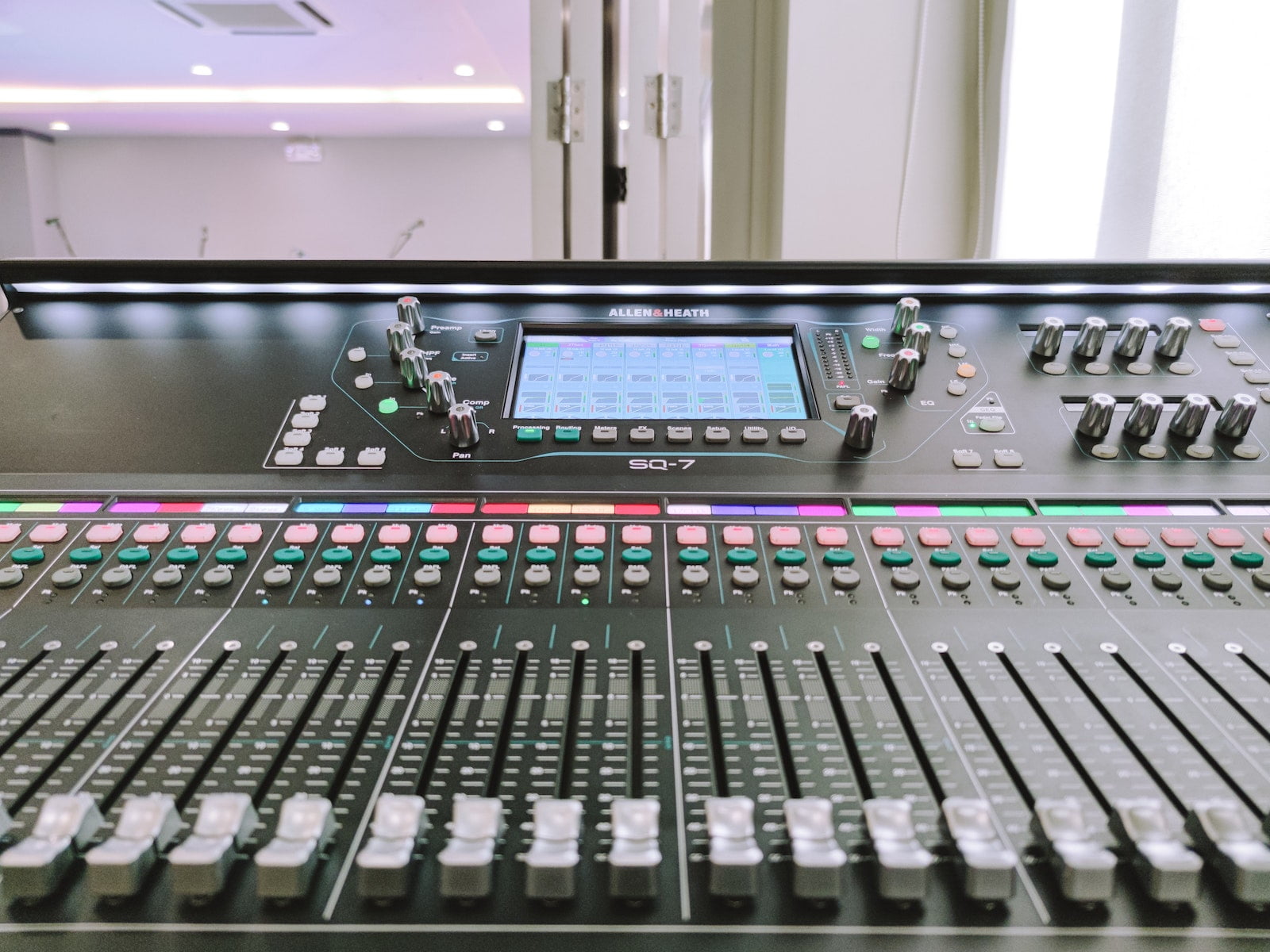

- Advantages of digital mixers:
- Digital mixers are generally more precise and consistent in their processing than analog mixers, since they are not subject to the limitations of physical components.
- Digital mixers can provide a wider range of processing functions and effects than analog mixers, since they can be programmed to provide any type of processing using software algorithms.
- Digital mixers can be more versatile and flexible than analog mixers, with features such as automated mixing with motorized faders, remote control, and digital networking.
- Disadvantages of digital mixers:
- Digital mixers may require more setup and configuration than analog mixers, since they often involve more complex routing and programming.
- Digital mixers may be less intuitive and hands-on than analog mixers, since they often require the user to interact with menus and screens rather than physical knobs and faders.
- Digital mixers may be more expensive than analog mixers, especially for higher-end models with advanced processing capabilities.
The choice between analog and digital mixers ultimately depends on the specific needs and preferences of the user. Analog mixers are a good choice for users who prioritize a warm, natural sound and hands-on control of the audio signals, and who are working with a limited budget. Digital mixers are a good choice for users who prioritize precision, consistency, and flexibility in their processing, and who are willing to invest in a more complex and feature-rich system. Additionally, some users may choose to use a hybrid system that combines both analog and digital processing, in order to take advantage of the strengths of both types of mixers.
In a hybrid system, analog signals can be routed through analog processors (such as EQs, compressors, and preamps) before being converted to digital signals and processed by digital mixers or other digital devices. This allows the user to take advantage of the warm, natural sound and hands-on control of analog processing, while still benefiting from the precision and flexibility of digital processing.
Similarly, digital signals can be processed by digital mixers or other digital devices before being converted back to analog signals and routed through analog processors. This allows the user to take advantage of the precision and flexibility of digital processing, while still benefiting from the warmth and coloration of analog processing.
A hybrid system can be configured in many different ways, depending on the specific needs and preferences of the user. For example, the user may choose to use a digital mixer with analog preamps and compressors, or an analog mixer with digital effects processors and digital recorders. The choice of components and the configuration of the system will depend on factors such as the type of audio being processed, the desired sound quality, and the budget and resources available.