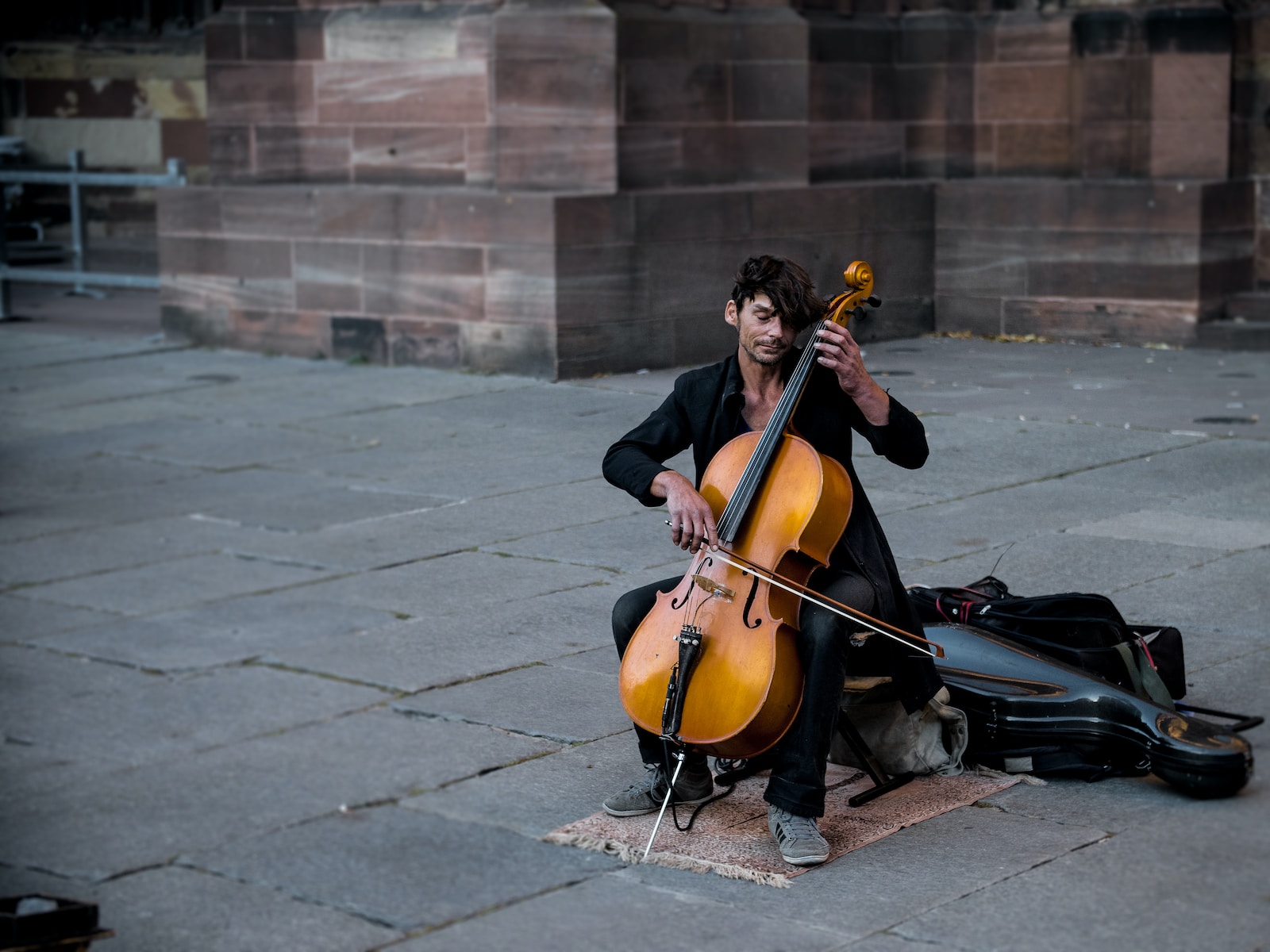
The cello, also known as the violoncello, is a bowed string instrument that is similar to the violin and viola but is much larger and produces a lower range of notes. It is commonly used in orchestras, chamber music groups, and as a solo instrument.
Here is an overview of the main components of a cello:
- Body: The body of the cello is made up of two parts, the top (or belly) and the back. The top is usually made of spruce, while the back can be made of maple, mahogany, or other hardwoods. The body is much larger than the violin and viola, with a long and wide waist. The body is also hollow to allow the sound to resonate and is shaped like a curved hourglass.
- Neck: The neck of the cello is attached to the body and extends upwards towards the headstock. It is usually made of maple or other hardwoods and is fitted with a fingerboard made of ebony or other hard woods. The neck holds the strings, and the fingerboard is where the musician places their fingers to change the pitch of the notes.
- Strings: The cello has four strings that are similar to the violin and viola in terms of tuning (C, G, D, A), but they are much thicker and produce a deeper, more resonant tone. The strings are stretched over the bridge and are held in place by the tailpiece.
- Bridge: The bridge of the cello is similar to the violin and viola in terms of shape and function. It is a thin piece of wood that is placed between the strings and the body of the cello. It is curved to allow the strings to vibrate freely and is held in place by the tension of the strings.
- Soundpost: The soundpost of the cello is also similar to the violin and viola in terms of function. It is a small, cylindrical piece of wood that is placed inside the body of the cello, underneath the treble side of the bridge. It helps to transfer the vibrations from the strings to the body of the cello, which amplifies the sound.
- Bow: The bow of the cello is similar to the violin and viola in terms of construction and materials. It is a long, slender stick made of wood, carbon fiber, or other materials. It is strung with horsehair and is used to play the strings of the cello. The bow is coated with rosin, a sticky substance that helps the bow grip the strings and produce a sound.
The cello produces a much lower range of notes than the violin and viola, and its larger size allows it to produce a rich and resonant tone. It is often used as a bass voice in orchestras and chamber music groups, and it is also used as a solo instrument. The cello’s deep and warm sound makes it well-suited for playing expressive and emotive music, and its versatility allows it to play a wide range of styles, from classical to rock and pop.