A sound system typically consists of the following components:
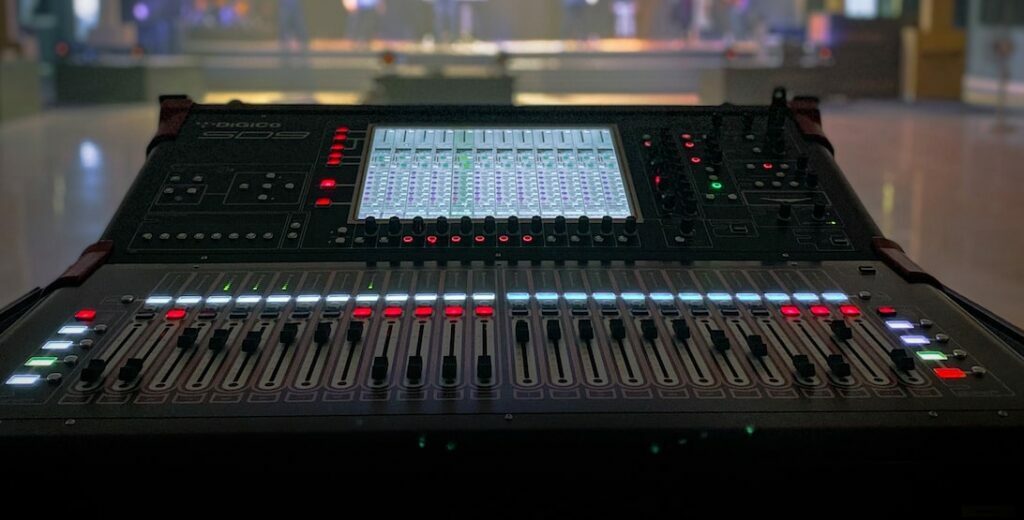

Mixer
A mixer is a device used in live sound settings to control the levels of different audio inputs, such as microphones and musical instruments. It allows the sound engineer to adjust the volume and tone of each input so that they can be heard clearly and in balance with each other. The mixer mixes all the audio inputs together into one output, which is sent to the amplifier and speakers to produce sound. This device is important in a live setting as it helps to create a clear and balanced sound mix for the audience.
Most popular live mixer brands including: Yamaha, Behringer, Allen & Heath, Midas, Mackie, Soundcraft, Presonus
See the products here

Amplifier
An amplifier is a device that makes the sound louder by boosting the strength of the audio signal. It takes the audio signal from the mixer and amplifies it, allowing the sound to be played through the speakers at a higher volume. An amplifier is essential in a sound system as it helps to produce sound that can be heard by a large audience.
See the products here

Speakers
Speakers are devices that play sound in live settings. They receive the amplified audio signal from the amplifier and convert it into sound waves that can be heard by the audience. Speakers are a crucial component of a live sound system as they are responsible for reproducing the audio for the audience to hear. In a live setting, Speakers are placed strategically to ensure that the sound is evenly distributed throughout the audience area.
See the products here

Microphones
A microphone is a device used to capture sound in live settings. It converts the sound it captures into an electrical signal that can be processed by the sound system. The microphone is essential in a live sound setting as it allows the sound of live performances, such as music or speech, to be captured and played through the speakers. The role of the microphone is to capture sound and turn it into an electrical signal so that it can be amplified and played through the speakers, allowing the audience to hear the performance.
See the products here

Cables
Cables are used to connect the different components of a sound system in a live setting. They transmit the audio signals between the mixer, amplifier, speakers, and other components, allowing the sound to flow from one component to another. The function of cables is to serve as a pathway for the audio signals, enabling the different components of the sound system to work together to produce sound. Without cables, the components of the sound system would not be able to communicate with each other and produce sound.
See the products here

Equalizer
An equalizer, or EQ, is a device used in sound systems to adjust the levels of different frequencies within the audio signal. It allows the sound engineer to fine-tune the sound by boosting or cutting specific frequencies. The role of an equalizer is to shape the sound by adjusting the balance of the different frequencies, allowing the sound engineer to achieve a desired sound. For example, an equalizer can be used to boost the bass frequencies for a fuller sound, or cut the high frequencies for a warmer sound. The equalizer is a powerful tool that can be used to adjust the tonal balance of the sound and enhance the overall listening experience.

Audio interfaces
An audio interface is a device used in live sound settings to connect external audio sources, such as musical instruments or sound sources from a computer, to the mixer. It converts the analog audio signals from the external sources into digital signals that can be processed by the mixer. The role of an audio interface in a live setting is to provide a way for the sound engineer to incorporate external audio sources into the live mix, allowing for a wider range of sound sources to be used in the performance. The audio interface acts as a bridge between the external audio sources and the mixer, allowing the sound engineer to control and manipulate the levels of the different audio inputs in the live mix. See the products here
These are the basic components of a sound system, and the specific components used can vary depending on the type of system and its intended purpose. For more complex sound systems, there are some additional components to consider including:

Crossovers
In a live setting, a crossover is used to separate the audio signal into different frequency ranges, such as bass, mids, and highs. These different frequency ranges can then be sent to separate amplifiers and speakers, allowing the sound engineer to control the levels of each frequency range independently. This can result in a clearer and more balanced sound, as the different frequency ranges can be adjusted to provide the right balance of bass, mids, and highs. The crossover is an important tool in live sound settings
Dynamic Processors
The role of dynamic processors is to help the sound engineer maintain a consistent and controlled level of sound. For example, a compressor can be used to prevent audio peaks from distorting by automatically reducing the volume of the audio signal when it exceeds a certain level. A limiter can be used to prevent the audio signal from exceeding a maximum level, preventing the sound from becoming too loud. A gate can be used to remove unwanted noise from the audio signal by automatically reducing the volume of the audio signal when it falls below a certain level.
Dynamic processors are an important tool in live sound settings, as they help to ensure that the sound is consistent and under control. By using dynamic processors, the sound engineer can maintain a consistent level of sound, even in challenging environments, and prevent audio peaks from distorting the sound.

Effects Processors
Effect processors are used to add effects to the sound of the performance. For example, reverb can be used to create a sense of space and depth, making the sound seem as though it is being performed in a large concert hall or other environment. Delay can be used to create a sense of distance, making the sound seem as though it is coming from further away. Chorus can be used to create a sense of depth and fullness, making the sound seem as though it is being performed by multiple musicians.
Effect processors are an important tool in live sound settings, as they allow the sound engineer to enhance the sound of the performance and create a more immersive listening experience. By using effect processors, the sound engineer can add depth, space, and texture to the sound, creating a more engaging and dynamic performance.

Power Conditioners
A power conditioner is a device used in live sound settings to improve the quality of the electrical power being supplied to the equipment. The role of a power conditioner is to protect the equipment from power surges, voltage spikes, and other electrical problems that can cause damage or affect the performance of the equipment.
In a live setting, a power conditioner is used to ensure that the electrical power being supplied to the sound equipment is of a consistent and high quality. The power conditioner filters out any electrical noise and fluctuations that can cause problems, such as crackling sounds or distortions. This helps to improve the overall performance of the sound equipment and reduce the risk of damage caused by electrical problems.
Wireless Systems
This allows the performer to move freely on stage, making it easier to engage with the audience and deliver an energetic performance. The wireless signal is received by a receiver connected to the sound mixer, where the signal is then processed and amplified for the audience.
Wireless systems are an important tool in live sound settings, as they allow the performers to move freely and engage with the audience without being restricted by cables.