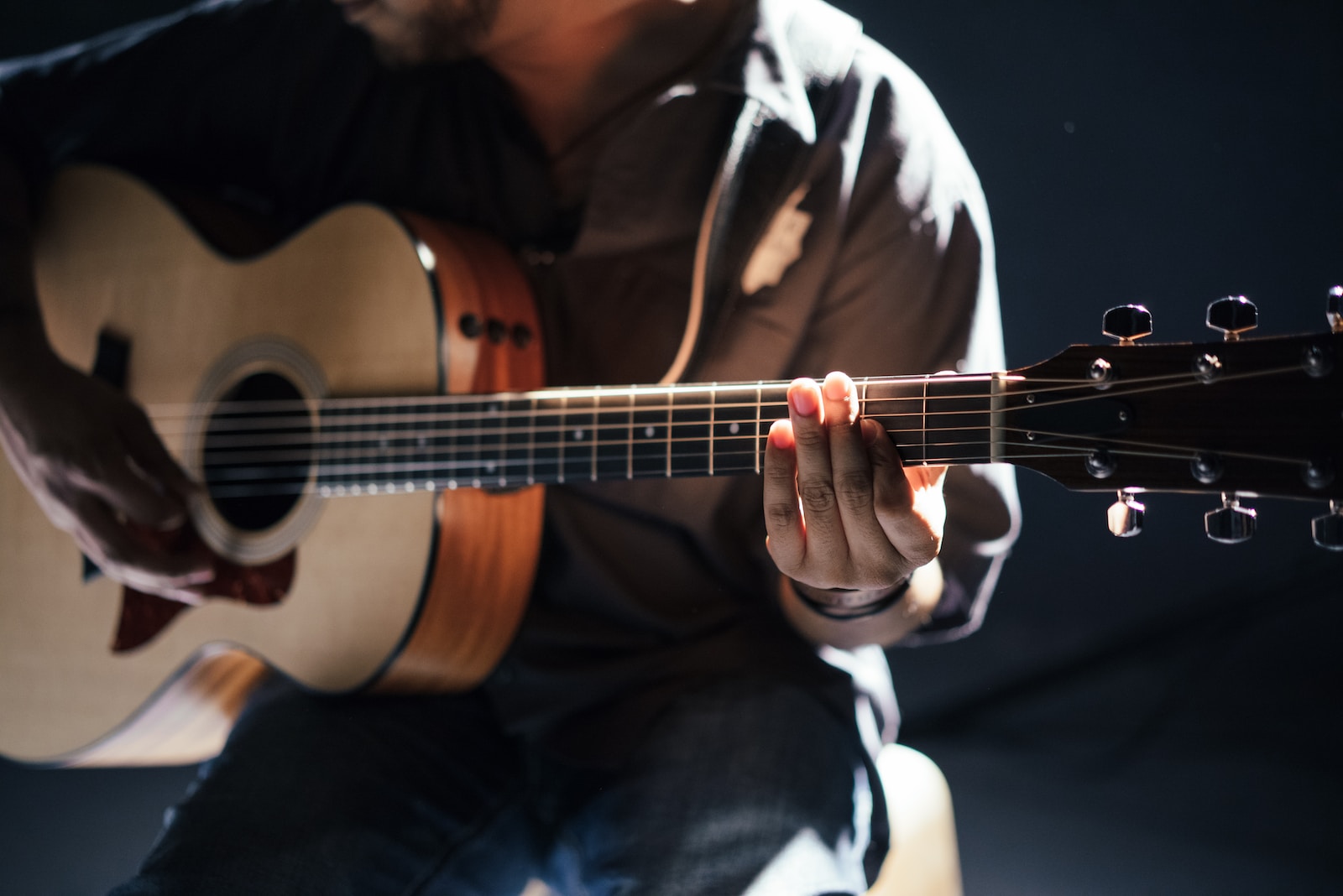
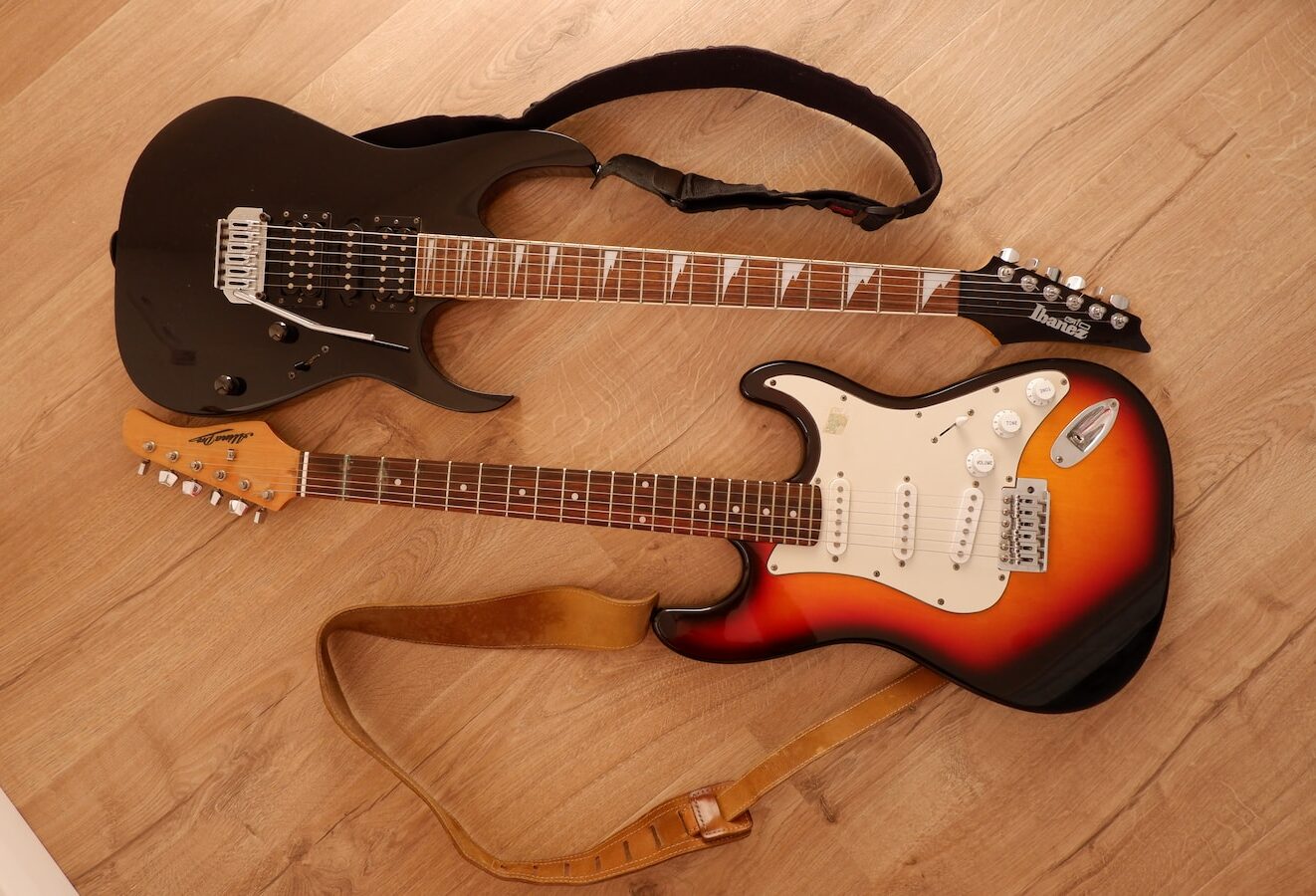
In general, guitar consist of several main components:
- Body: The main part of the guitar, which holds the other components and provides a surface for the strings to vibrate against.
- Neck: The long, narrow part of the guitar that supports the fretboard and holds the strings in place. It typically has frets (small metal bars) embedded into the fretboard, which help the player produce different notes.
- Headstock: The top part of the guitar’s neck, which holds the tuning pegs.
- Tuning pegs: Small, cylindrical pegs that are used to adjust the tension on the strings, thereby changing their pitch.
- Bridge: A structure that anchors the strings to the body of the guitar and helps transmit their vibrations to the soundboard.
- Strings: Thin, flexible wires that run the length of the guitar and are tuned to specific pitches by adjusting the tension using the tuning pegs.
- Fretboard: The flat, usually wooden surface that sits atop the neck and contains the frets.
- Nut: A small strip of material (often plastic or bone) that sits at the top of the fretboard and helps to space the strings out evenly.
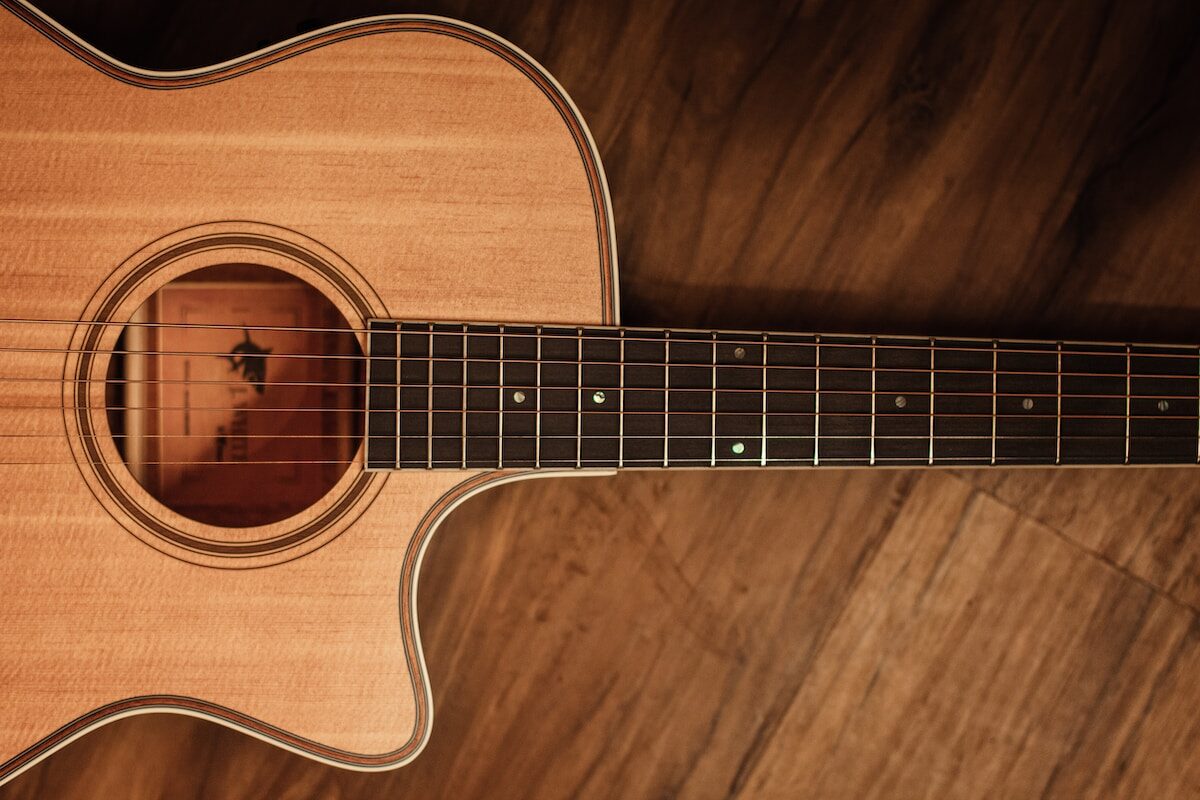

Components specific to acoustic guitars
In addition to the components common to all types of guitars, acoustic guitars also have several components that are specific to their design and function, including:
- Soundhole: A circular opening on the front of the guitar’s body that allows the sound to escape and be heard by the listener.
- Soundboard/top: The thin, flat piece of wood that covers the front of the guitar’s body and is responsible for producing the sound.
- Bracing: Internal support structures that reinforce the soundboard and help to distribute the vibrations of the strings evenly across the guitar’s body.
- Saddle: A small strip of material (often plastic or bone) that sits on the bridge and helps to space the strings out evenly and transfer their vibrations to the soundboard.
- Pickguard: A thin, protective layer of material (often plastic) that is attached to the front of the guitar’s body to protect it from scratches and other damage caused by the player’s strumming or picking.
- Binding: Decorative strips of material (often plastic or wood) that are used to cover the edges of the guitar’s body and give it a finished, polished appearance.
- Rosette: A decorative ring around the soundhole that adds visual interest to the guitar’s design.
- Heel: The thickened portion of the guitar’s neck where it joins the body, providing additional strength and support.
Components specific to electric guitars
Electric guitars also have some components that are specific to their design and function, in addition to the components shared by all guitars. These include:
- Pickups: As mentioned earlier, pickups are electromagnetic devices that detect the vibrations of the strings and convert them into electrical signals, which can then be amplified and heard through speakers.
- Output jack: A small, circular port on the guitar’s body where a cable can be plugged in to connect the guitar to an amplifier or other sound system.
- Volume and tone controls: Knobs or switches that allow the player to adjust the volume and tone of the guitar’s sound, often in combination with the pickup selector switch.
- Pickup selector switch: A switch that allows the player to choose which pickup or combination of pickups is active.
- Tremolo bridge: A bridge that allows the player to manipulate the tension on the strings, creating a vibrato or “whammy” effect.
- Control knobs: Some electric guitars may have additional control knobs or switches for effects like distortion, delay, or reverb.
- Fretboard inlays: Many electric guitars feature decorative inlays on the fretboard, such as dots or other shapes, to help the player orient themselves on the neck.
It is important to understand the different components of a guitar because it can help you make informed decisions when purchasing or maintaining a guitar. Having a basic understanding of the different parts can also help you communicate effectively with guitar technicians or repair specialists if you need to have work done on your instrument.
Additionally, understanding the different components of a guitar can deepen your appreciation and understanding of the instrument, and allow you to better appreciate the craftsmanship and artistry that goes into building and even playing a high-quality guitar.